Product Overview
Product Overview
IGF-1 LR3 Overview
IGF-1 LR3 (Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Long R3) is a synthetic analogue of IGF-1, a naturally occurring growth factor in the human body. IGF-1 is an important mediator of growth hormone (GH) effects, promoting muscle growth, repair, and regeneration. The “Long R3” modification significantly increases its half-life and bioavailability, making it more potent and longer-acting than natural IGF-1.
Peptide Structure
Research Applications
In research studies, IGF-1 LR3 has demonstrated potential in:
- Promoting muscle hypertrophy and preventing atrophy in animal models
- Enhancing wound healing and tissue repair
- Improving recovery following nerve injuries
- Investigating its role in neuroprotection and cognitive function
Due to its extended half-life, IGF-1 LR3 remains active in the body for longer periods, making it a preferred variant for research compared to native IGF-1.
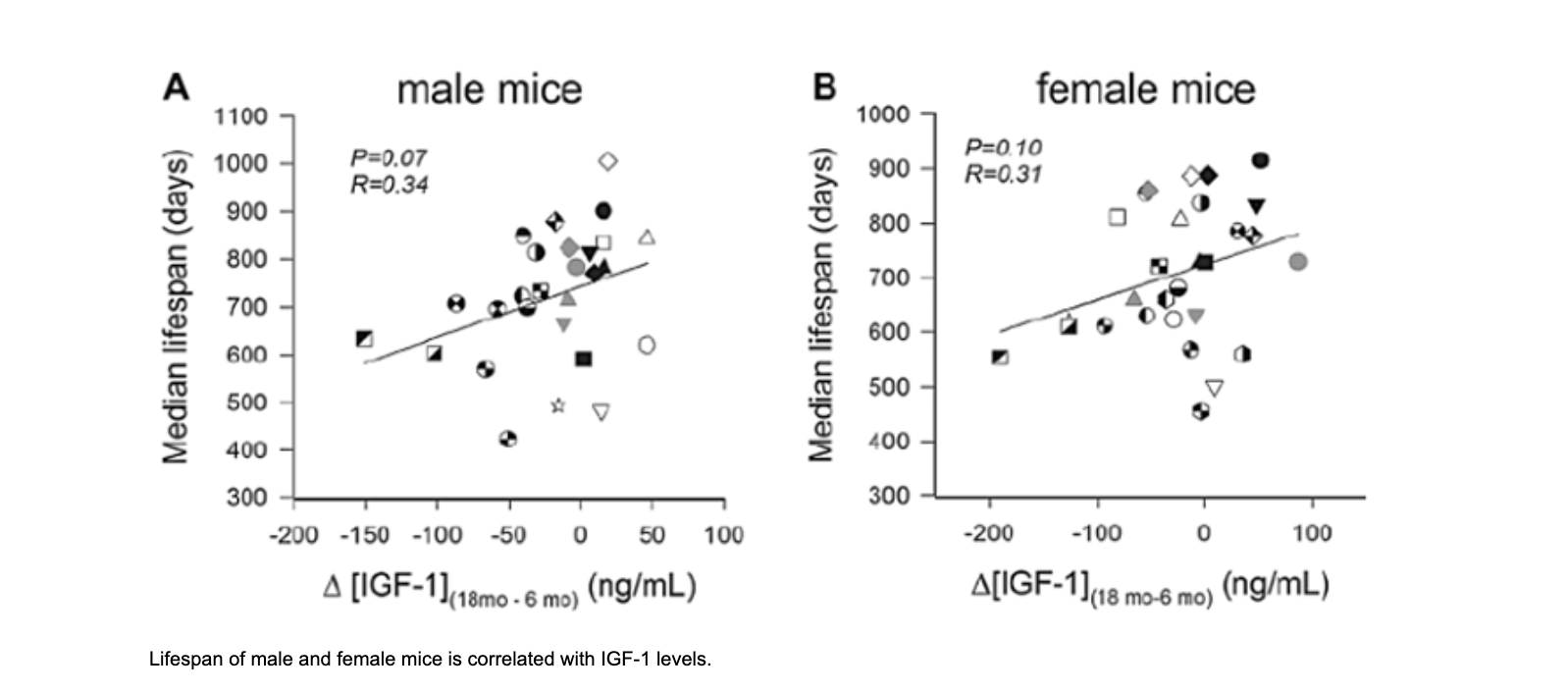
Longevity Research
IGF-1 LR3 is also under investigation for its potential role in longevity and age-related diseases. Research has explored its ability to mitigate sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss), improve bone density, and contribute to overall tissue maintenance and regeneration in aging populations.
Referenced Citations
- “Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cell Secreted IGF-1 Protects Myoblasts from the Negative Effect of Myostatin.” [Online]. Available: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2014/129048/
- N. Li, et al., “Myostatin Attenuation In Vivo Reduces Adiposity, but Activates Adipogenesis,” Endocrinology, vol. 157, no. 1, pp. 282–291, Jan. 2016.
- E. Corpas, et al., “Human growth hormone and human aging,” Endocr. Rev., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 20–39, Feb. 1993.
- W. E. Sonntag, et al., “Diverse roles of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in mammalian aging,” J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci., vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 587–598, Jun. 2012.
- “IGF-I/IGFBP system: metabolism outline and physical exercise.” [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22714057
- B. Y. Hanaoka, et al., “Implications of glucocorticoid therapy in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies,” Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 448–457, Aug. 2012.
- A Philippou, et al., J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact, 2007 [Semantic Scholar]
- A Philippou, et al., In vivo, 2009 [Iiar Journals]
All Articles and Product Information Provided On This Website Are For Informational and Educational Purposes Only.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.