Product Overview
Product Overview
What Is Epithalon?
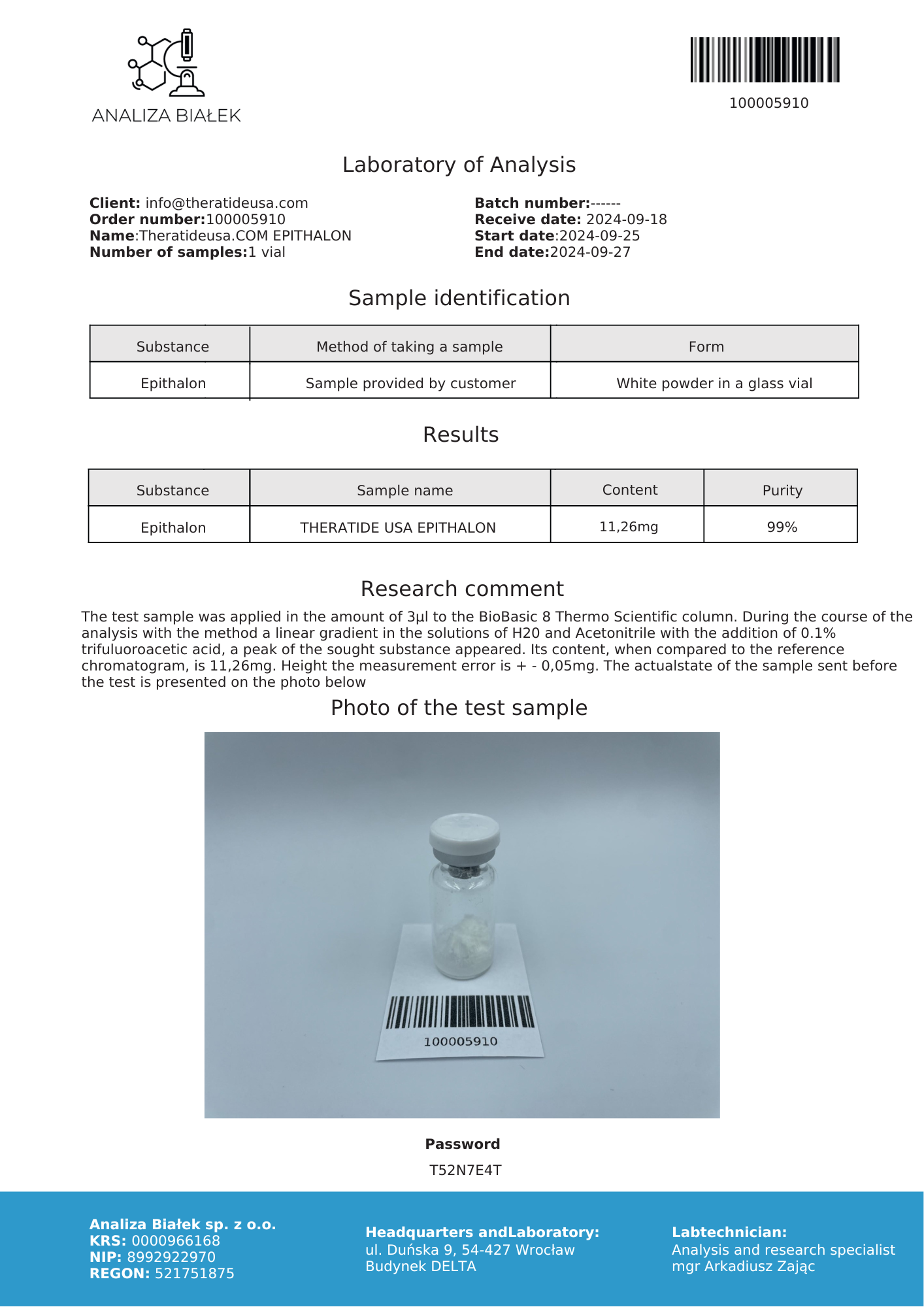
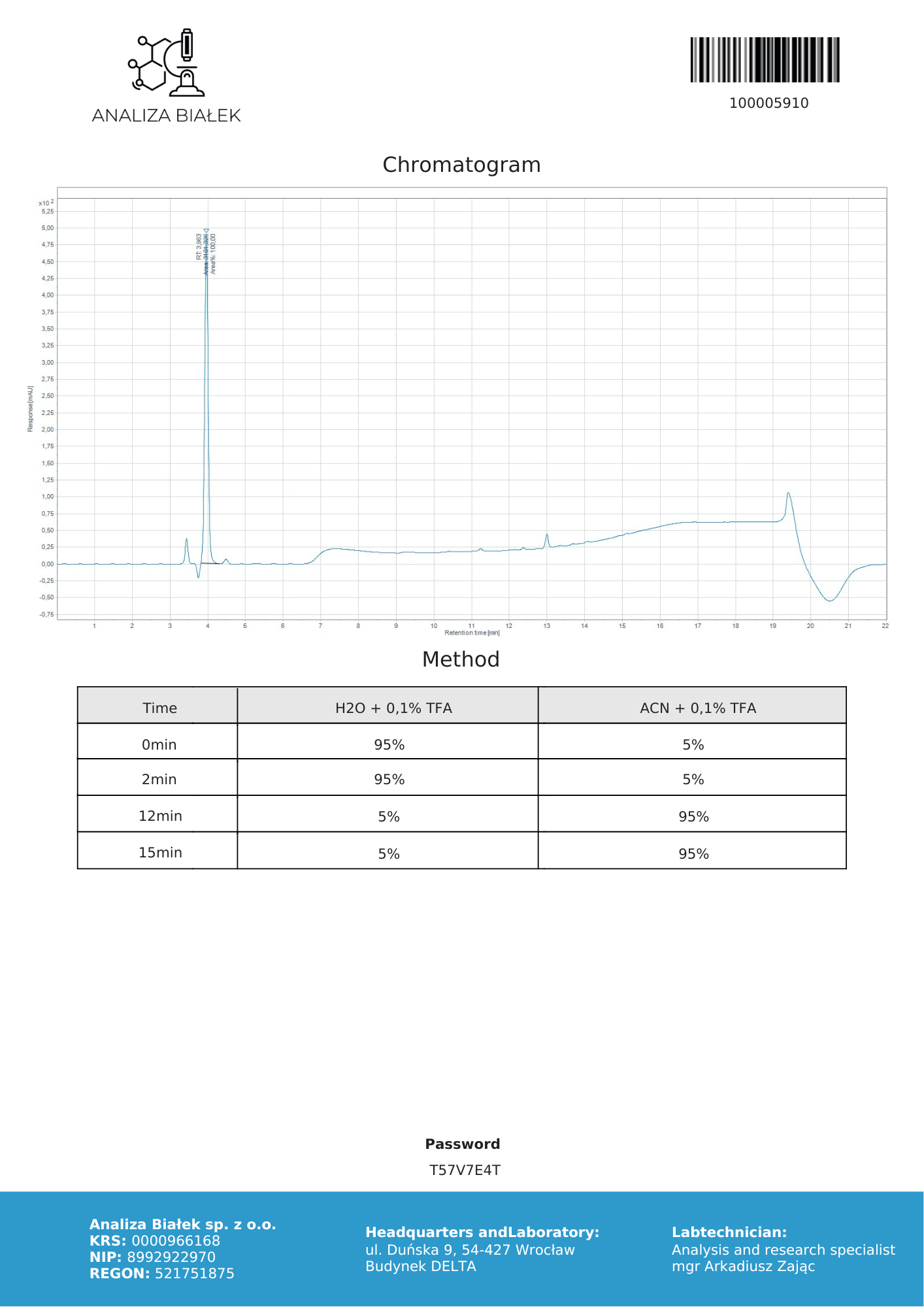
Epithalon (also known as Epitalon, Epithalone or Epithalamin) is a short synthetic peptide known to activate the telomerase enzyme and stimulate melatonin release. First developed in Russia in the 1980s, epithalon has been shown to delay age-related changes in reproductive and immune systems and increase the life span of mice and rats. Though it is primarily of interest in anti-aging research, epithalon has shown significant effects in certain types of cancer, infectious disease, and in DNA regulation.
Epithalon Structure
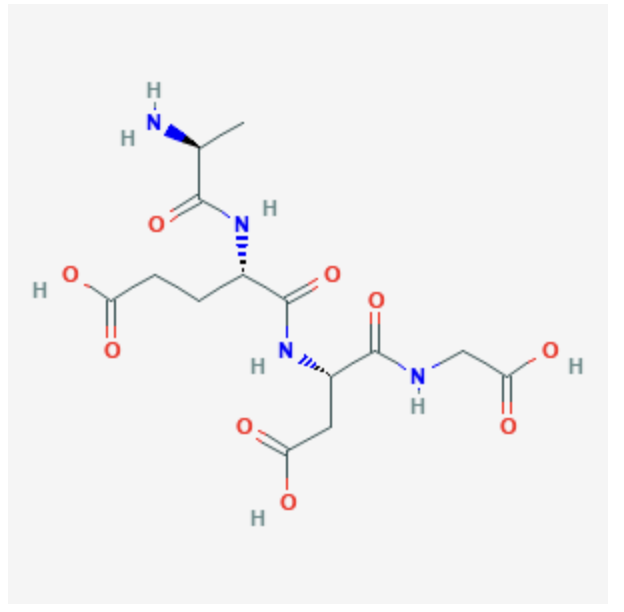
Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Molecular Formula: C14H22N4O9
Molecular Weight: 390.349 g/mol
PubChem CID: 219042
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
Epithalon Research
1. The Role of Telomerase in the Anti-Aging Effects of Epithalon
Research in insects and rodents has shown that epithalon prolongs life by eliminating free radicals and activating telomerase, which protects telomeres and prevents DNA damage. In mice prone to heart disease and cancer, epithalon increased lifespan by up to 27%.
2. Epithalon and DNA Activation
Epithalon interacts directly with DNA to turn on and enhance the expression of genes like CD5, IL-2, MMP2, and Tram1. This enhances immune system function and tissue maintenance while reducing age-related decline. Epithalon also boosts interferon gamma in aging lymphocytes, improving immune defense.
- CD5 – Leads to immune cell differentiation
- IL-2 – Regulates white blood cell production
- MMP2 – Maintains extracellular matrix and reduces inflammation
- Tram1 – Enhances protein production
- AANAT – Boosts melatonin production
- pCREB – Regulates circadian rhythm and anti-tumor effects
- Telomerase – Increases cell longevity
3. Epithalon and Skin Health
Epithalon activates fibroblasts and enhances MMP2 gene activity, improving skin repair and reducing the effects of aging on skin structure.
4. Epithalon and Tumor Growth
Research shows epithalon reduces tumor growth and metastasis in rats, and may play a role in regulating genes (like PER1) involved in cancer progression.
5. Epithalon and Melatonin Secretion
Epithalon restores melatonin secretion and circadian rhythm in aged animals by regulating AANAT and pCREB genes.
6. Epithalon and Eyesight
In rat studies of retinitis pigmentosa, epithalon improved outcomes in 90% of cases, preserving retinal structure and function.
Referenced Citations
- V. N. Anisimov et al., “Pineal peptide preparation epithalamin increases the lifespan of fruit flies, mice and rats,” Mech. Ageing Dev., 1998.
- V. K. Khavinson et al., “Epithalon peptide induces telomerase activity and telomere elongation in human somatic cells,” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2003.
- T. A. Dzhokhadze et al., “Functional regulation of genome with peptide bioregulators,” Georgian Med. News, 2013.
- V. N. Anisimov et al., “Effect of Epithalon on biomarkers of aging,” Biogerontology, 2003.
- V. K. Khavinson et al., “Short cell-penetrating peptides: gene promoter interactions,” Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2013.
- N. S. Lin’kova et al., “Peptide Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly and immune response,” Adv. Gerontol., 2012.
- N. I. Chalisova et al., “Short peptides stimulate skin regeneration,” Adv. Gerontol., 2014.
- More available upon request.
All Articles and Product Information Provided On This Website Are For Informational and Educational Purposes Only.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat, or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.